This article has been just updated: January 16, 2024
There are many reasons why an individual might desire to keep their online activities private. In order to accomplish this feat, there are two prime options available. One is to use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) service. The other is to download and employ the Tor browser when going online.
While the functionality of these two alternatives overlaps considerably, they are not totally equivalent. There are significant differences in what an online user can do when using each of these methods of concealing their online movements. We are going to look at various features of these tools and compare their utility in performing different actions online.
Why Would I Want to Remain Anonymous Online?
Here are some of the reasons that you would want to use Tor or a VPN service when you are online. In some cases, one of the solutions is superior to the other and we will look at those discrepancies later in the article.
- Simply as a means of protecting your privacy
- Hiding Internet activity from your ISP
- Safely using public WiFi
- Bypassing government or organizational censorship
- Preventing tracking by Google and other online advertisers
- Performing sensitive research anonymously
- Accessing torrent sites
- Performing whistleblowing and investigative journalistic activities
- Accessing sites on the deep web or dark web
This is not an exhaustive list and you may have other reasons why you prefer to keep your online movements to yourself. One thing is for certain, most of us would not tolerate someone following us around the city and noting every action we took.
If you don’t take steps to maintain online anonymity, you are basically accepting the fact that you are being tracked from the time you start surfing until you shut down your browser.
Differences Between Tor and a VPN Service
Both a VPN service and the Tor browser can provide anonymity while you are online. They mask your identity in different ways, as we will briefly describe.
Tor browser
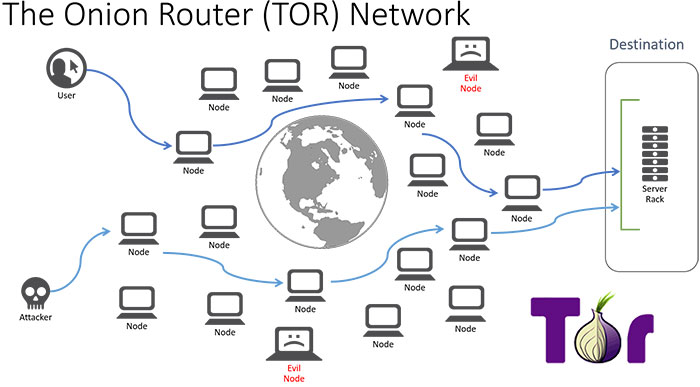
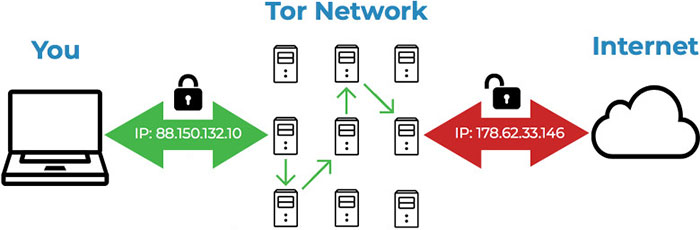
When using the Tor browser your Internet activity is routed through different servers in the Tor network. Each server only knows where the traffic is coming from and where it is going. The IP that originated the online activity, which is the IP of your computer, is obscured by the many servers your Internet connection passes through. This is how the Tor browser keeps your identity private.
VPN Service
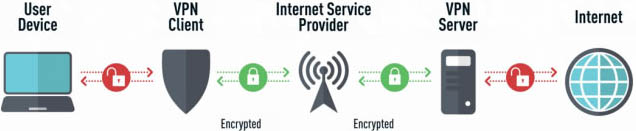
In a somewhat similar manner, a VPN routes your online activity through one of its stable of VPN servers. Once you are connected to the VPN server, that becomes the IP address which will be visible to sites that you visit. VPNs claim that logs are not kept, but the potential exists that there is some logging that indicates your machine was connected with a given VPN server. In some cases, this information could possibly be made available to authority figures which would negate the protection that you believed was in place.
Let’s look at some specific ways that Tor and a VPN service differ in what they offer and what types of activities they can perform:
1 Accessing a Variety of Websites
The surface web comprises a small fraction of the accumulated information that is available on the Internet. All of the websites that can be reached through your traditional browser are part of the surface web. Using a VPN service or the Tor browser allows you to reach the majority of these sites. Some websites may prevent access from VPN servers if they can identify them. Tor does not have these restrictions and can get to all of the surface websites.
Tor really differentiates itself from a VPN service with its ability to access deep and dark websites. Using the Tor browser you can reach many more websites than with a traditional browser and a VPN service. That being said, caution needs to be exercised as many of the sites below the surface web may promote illegal activities and be prone to spreading malware.
2 Accessing Certain Types of Content
The Tor browser blocks plugins like Flash, Quicktime, and RealPlayer. If the sites you intend to visit require these types of additions to your browser, then you should not use Tor.
Stick to a VPN and a more traditional browser like Chrome or Safari if you require the use of plugins while online.
3 Torrenting
This one is simple. Tor documentation recommends not using the browser for torrenting as it can expose your IP address. If you engage in downloading content from torrent sites, you really should be using a VPN service. Many jurisdictions have issues with the way copyrighted materials are distributed through torrents, and a VPN will keep you anonymous and allow you to download whatever you like without your ISP or anyone else knowing.
4 Connection Speed
One of the benefits of using a VPN service is that you will often experience better download performance than when you are simply using your ISP. A known problem with ISPs is the tendency to throttle your download capabilities, especially if you are accessing torrent sites and performing large downloads.
Based on the way the Tor browser operates by routing your online activity through multiple servers to protect anonymity, its performance is noticeably slower than a traditional browser such as Chrome or Firefox.
5 Price
The Tor browser is available for all major computing platforms as a free download. While there are free VPN services, the more reputable services do entail some financial investment.
This is usually in the form of a monthly subscription fee which can be minimized by signing up for an extended period of time. If you choose to trust your online privacy to a VPN, it is worth the money to choose a reliable one. For example, the best VPN – NordVPN costs $2.99 per month.
6 Subverting Censorship
Either a VPN service or the Tor browser can be used to subvert government or organizational censorship. Both methods allow you to access sites which authorities may have decreed are restricted and are not available through your ISP and a regular browser. Tor gives you the flexibility of accessing the .onion sites which can be used to access news sites in censored locales. This is not a feature of any VPN service.
7 Concealing Online Intentions
If you are in a situation such as a business or government setting where the contents of your computer is monitored, employing Tor may not be a good choice. Though there are many legitimate uses of the Tor browser, it can set off alarm bells for security personnel who may question why you decided to install it on your machine.
You might have had intentions of using the browser to perform whistleblowing activities to reveal some sensitive information that deserves to be made public. The presence of the Tor browser on your computer can have the effect of causing greater scrutiny of your activities. Using a VPN is a more accepted method of maintaining privacy and protecting your identity and may not raise as many red flags as a download of Tor.
Should I Use Tor or a VPN Service?
As you can see from the preceding discussion, your selection depends on the online activity in which you will be engaging. For users who wish to torrent and are concerned with download speed, a VPN is the way to go. If you are interested in the additional sites that are available through the deep and dark web, then Tor is your only real choice.
If your goal is simply to protect your online movements and remain anonymous to your ISP and other prying eyes, either Tor or a VPN will work. Both will mask your machine’s ISP address which is how you are identified online. By employing one of these methods every time you surf the web, you can protect your privacy and hide your identity.
FAQ
How do TOR and a VPN protect online privacy differently?
TOR, short for The Onion Router, employs a network of volunteer-run servers to anonymize your internet connection by directing traffic through multiple layers of encryption, akin to layers of an onion. With each relay, the traffic is encrypted and decrypted, making the source virtually untraceable. A VPN (Virtual Private Network), on the other hand, secures your internet connection by routing it through a server operated by the VPN provider, encrypting data from your device to that server. As a result, your IP address is hidden, and your data is protected from eavesdropping.
What are the key advantages of using TOR for online privacy?
The key advantages of using TOR are enhanced anonymity and the ability to bypass censorship. TOR makes it extremely difficult for anyone to trace your internet activities back to you. It’s also effective in circumventing internet filters and accessing content that may be blocked in certain countries.
How does a VPN contribute to online privacy?
A VPN enhances your online privacy by providing a secure tunnel between your device and the internet. This protects your data from hackers on the same network, masks your IP address, and can prevent your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or governments from monitoring your online activities.
Is TOR alone enough to ensure complete online anonymity?
While TOR provides a high level of anonymity, no system is completely foolproof. Potential vulnerabilities could include end-point security issues where the data leaves TOR and enters the public internet, as well as the possibility of malicious TOR nodes compromising privacy.
Can VPNs protect against all types of online surveillance?
No, VPNs are not immune to all types of surveillance. Some advanced surveillance methods employed by governments might still detect online activities through deep packet inspection techniques, or potentially compromised VPN services could leak information.
What are the limitations when using TOR for online activities?
The limitations of using TOR include slower internet speeds due to traffic being routed through multiple nodes, and some websites blocking access from TOR nodes. Moreover, downloading files over TOR can potentially reveal your non-TOR IP address, thus risking your anonymity.
What factors should be considered while selecting a VPN service provider?
When selecting a VPN service provider, consider factors such as reputation, the strength of encryption protocols, no-logging policies, server locations, speed, compatibility with your devices, customer support, and cost. It’s essential to do thorough research on the VPN providers like checking VPNmentor for reviews and comparisons.
Are there any legal issues associated with using TOR?
In most countries, using TOR is entirely legal. However, because of its association with the dark web and illegal activities, some governments scrutinize TOR users more closely. It’s crucial to understand the laws governing TOR usage in your area.
Can a VPN affect internet connection speeds?
Yes, a VPN can sometimes affect your internet connection speed due to encryption overhead and the distance your data has to travel to reach the VPN server. However, the impact is typically negligible with high-quality VPN services.
How can combining TOR and a VPN enhance privacy?
Combining TOR and a VPN can enhance privacy by adding multiple layers of security. Using a VPN with TOR (known as TOR over VPN) provides anonymity of TOR along with the encryption and IP masking of the VPN. This makes it even more challenging to trace online activity back to the user.
Is it safe to transmit sensitive information over TOR?
Transmitting sensitive information over TOR is not recommended due to the potential risk of encountering a compromised exit node, which could potentially expose the data being transmitted. For sensitive transactions, a secured, reputable VPN may be preferable.
Do VPNs protect against malware and phishing attacks?
While VPNs are primarily designed to encrypt data and hide your IP address, some VPN providers offer additional security features that can help protect against malware and phishing attacks. However, a reputable antivirus and safe browsing habits should also be part of your security measures.
How do I configure TOR to maximize privacy?
To maximize privacy on TOR, ensure you are using the latest version of TOR Browser, avoid installing additional browser extensions, avoid using browser-based services that require personal information, adjust the security settings within TOR Browser to the highest level, and never open documents downloaded through TOR while online.
Does using a VPN make someone completely anonymous online?
No, using a VPN does not make someone completely anonymous, as there may still be ways to trace activity back to a user, notably if the VPN keeps logs or if the user’s identity is compromised through other means such as cookies, accounts they log into, or browser fingerprinting.
Can using TOR or a VPN allow access to geo-restricted content?
Yes, both TOR and VPNs can potentially enable access to geo-restricted content. A VPN can easily allow you to choose a server in a country where the content is available, while TOR might also bypass geo-restrictions, but with less control over exit nodes.
What are the best practices for ensuring that a VPN maintains privacy?
To ensure a VPN maintains privacy, choose services that offer strong encryption, maintain no logs, offer a kill switch feature that cuts off internet access if the VPN connection drops, and regularly update their software. Reliability and transparency of the VPN provider are also critical.
Can I use TOR for everyday internet browsing?
Yes, you can use TOR for everyday browsing, but expect slower speeds and some websites may not function properly due to TOR blocking scripts that compromise privacy. For better performance on websites you trust, a VPN might be more suitable.
Is it necessary to pay for a VPN service, or are free versions adequate?
While free VPNs are available, they often come with trade-offs such as data limits, slower speeds, fewer server options, and questionable privacy policies. For robust privacy protection, a reputable paid VPN service is generally recommended. You can explore options at PrivacyTools.
What should I avoid doing while connected to TOR or a VPN to maintain privacy?
When connected to TOR or a VPN, you should avoid logging into accounts tied to your real identity, downloading files without a secure connection, enabling or allowing JavaScript on unknown websites (for TOR), using services that store cookies or track users, and disregarding the VPN’s security settings and policies.
How regularly should I update my VPN software?
Regularly updating your VPN software is crucial to protect against vulnerabilities and maintain privacy. Set your application to update automatically or check for updates frequently to ensure you’re using the most secure version available.